Understanding the Basics of Retargeting in Paid Advertising:

Retargeting, also known as remarketing, is a powerful technique in paid advertising that allows you to reconnect with users who have previously interacted with your website or ads. These users have shown interest in your products or services but didn’t convert. Retargeting helps keep your brand top-of-mind and encourages users to return and complete their purchase or desired action. This blog will explain the basics of retargeting and how to implement it effectively in your paid advertising strategy.
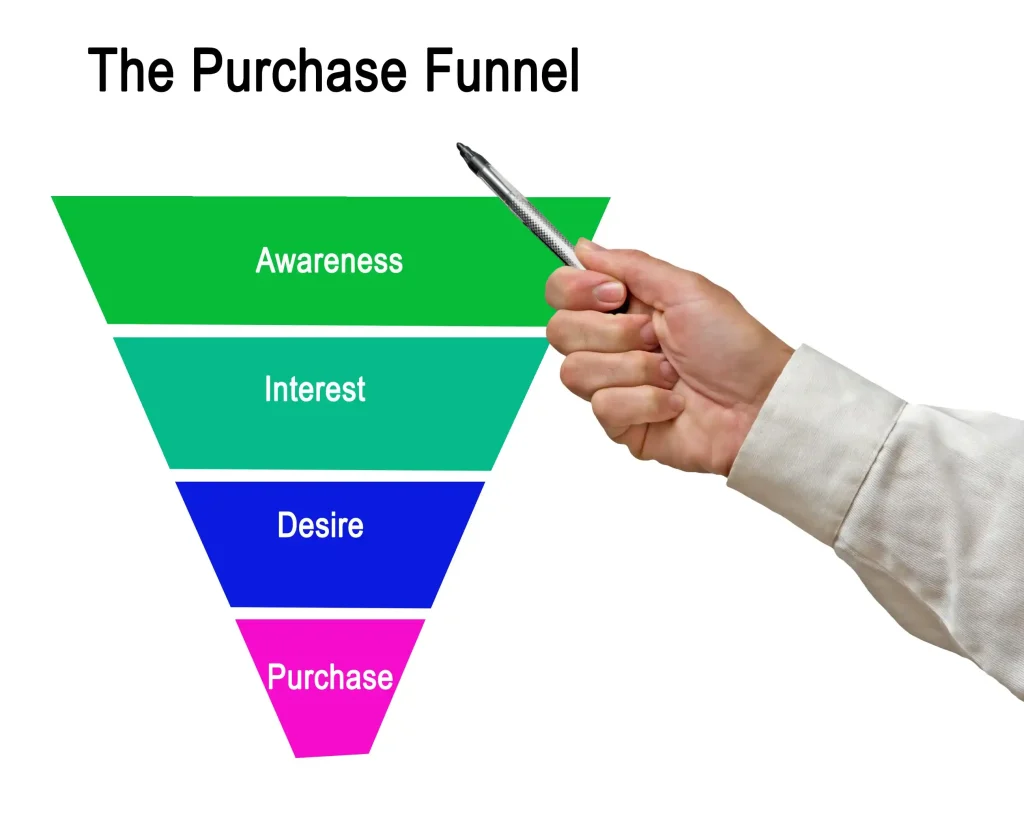
What is Retargeting?
Retargeting is the practice of displaying targeted ads to users who have already visited your website, interacted with your ads, or engaged with your brand in some way. It’s based on the idea that people who have shown interest in your product or service are more likely to convert if they are reminded about it.
Retargeting works by placing a cookie (a small piece of code) on the user’s browser when they visit your site. This cookie tracks their behavior and allows you to display ads to them as they browse other websites or social media platforms.
Why Retargeting Matters:
-
Increased Conversion Rates: Retargeting allows you to reach users who are already familiar with your brand. Since these users have previously interacted with your site, they are more likely to convert on a second visit.
-
Cost-Effective: Retargeting ads often have lower costs per click (CPC) compared to standard display ads. This is because you’re targeting a more qualified audience that has already shown interest in your product or service.
-
Brand Recall: By staying in front of potential customers with retargeting ads, you increase brand recall and help keep your business top-of-mind. Even if they don’t convert immediately, they may return later when they’re ready to purchase.
-
Customization: Retargeting allows you to segment your audience based on their behavior and serve them personalized ads. For example, if someone added a product to their cart but didn’t complete the purchase, you can show them ads reminding them of the item.
How Retargeting Works:
Retargeting works through cookies or pixel tracking. Here’s how it typically works:
-
User Visits Your Website: A user visits your website and interacts with your content, products, or services. The retargeting pixel or cookie is placed on their browser.
-
User Leaves the Website: After leaving your site, the user continues to browse other websites or social media platforms.
-
Retargeting Ads Appear: Your retargeting ads are shown to the user as they browse other sites, encouraging them to return and complete the desired action (e.g., making a purchase).
There are different types of retargeting campaigns, including:
-
Standard Retargeting: Shows ads to users who have visited your website, encouraging them to return.
-
Dynamic Retargeting: Displays personalized ads based on the exact products or services the user interacted with on your website.
-
Social Media Retargeting: Displays ads on social media platforms (such as Facebook and Instagram) to users who have visited your website.
Best Practices for Retargeting:
-
Segment Your Audience: Not all visitors are the same. Segment your audience based on their behavior, such as those who visited specific product pages, abandoned their cart, or viewed content. This allows you to create more targeted and relevant ads.
-
Create Compelling Ad Copy: Craft ad copy that is relevant to the user’s previous interactions with your website. For example, if a user abandoned a cart, your ad should highlight the product they left behind and offer a special discount or incentive.
-
Use Frequency Caps: Avoid bombarding users with the same retargeting ads too frequently, as this can lead to ad fatigue and annoy potential customers. Set frequency caps to limit how many times a user sees your ad.
-
Time Your Retargeting Ads: Timing matters in retargeting. If someone abandoned their cart, showing them an ad within a few hours or days of their visit can be more effective than waiting too long. Consider the user’s buying cycle when timing your ads.
-
Leverage Dynamic Ads: Dynamic retargeting ads show users products or services they viewed but didn’t purchase. These ads are personalized to the user’s behavior and can lead to higher conversion rates.
Conclusion:
Retargeting is an essential strategy in paid advertising that can significantly improve your conversion rates and help you re-engage users who have already shown interest in your products or services. By segmenting your audience, creating personalized ads, and optimizing your retargeting campaigns, you can maximize your ROI and drive more conversions. Incorporating retargeting into your overall advertising strategy is a powerful way to stay connected with potential customers and increase the likelihood of turning them into loyal buyers.